How Digital Image Processing Shapes Modern Photography
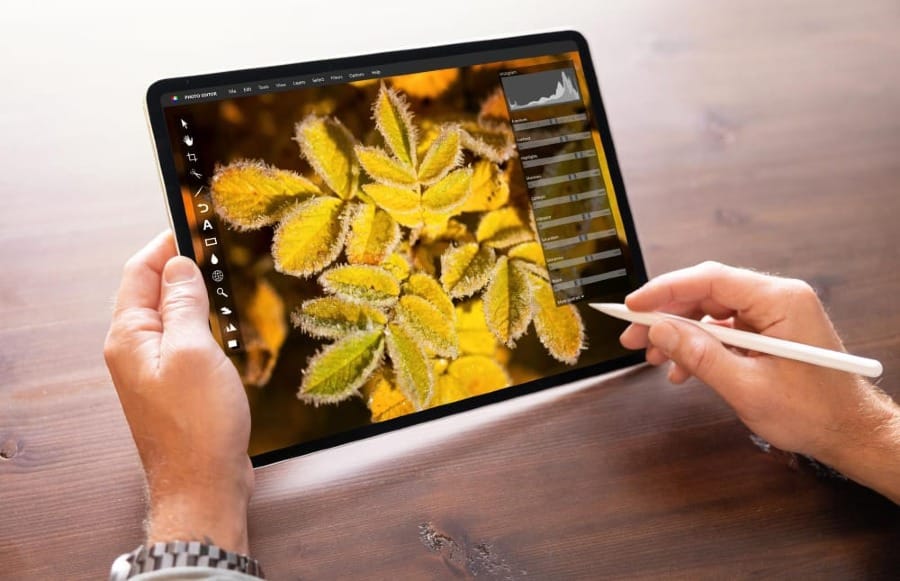

1. Introduction to Digital Image Processing
1.1 What is Digital Image Processing?
Digital image processing refers to the use of computer algorithms to perform image manipulation on digital images. It involves a series of techniques designed to enhance image quality, correct flaws, and extract meaningful information. Unlike traditional photo editing, digital image processing is rooted in scientific principles, enabling precise control over various aspects of an image. From adjusting brightness and contrast to applying complex filters, this process forms the backbone of modern photography workflows.
1.2 The Evolution of Photography Through Digital Tools
Photography has come a long way from the days of analog film and darkrooms. The introduction of digital cameras revolutionized how images are captured, stored, and shared. However, the ability to process these images digitally has brought about an even greater transformation. Digital image processing allows photographers to overcome limitations like poor lighting, low resolution, or noise in a way that was previously unimaginable. With advancements in software and hardware, this technology continues to reshape photography, making it more accessible and versatile than ever.
Affiliate Disclaimer
This blog post may include links to affiliate sites. If you click on an affiliate link and make a purchase, we may earn a small commission or receive other compensation at no extra cost to you. Please note that many of the links on our site are affiliate links. Our use of these links does not impact the products, services, or websites we recommend to you. This disclaimer covers all forms of communication with you, including our website, email, phone, social media, products, and other platforms.
1.3 Why Digital Image Processing Matters in Modern Photography
In today’s fast-paced world, photographers need tools that not only streamline their work but also enhance creativity. Digital image processing meets this need by offering unparalleled flexibility and control. It enables photographers to correct imperfections, highlight their artistic vision, and adapt their images for different purposes—be it social media, print, or commercial projects. Additionally, digital image processing bridges the gap between science and art, empowering photographers to achieve results that reflect their unique style. As photography evolves, mastering this technology is becoming essential for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
2. The Core Principles of Digital Image Processing
2.1 Image Acquisition: From Capture to Pixels
Digital image processing begins with image acquisition, which is the process of capturing an image and converting it into a digital format. This step is crucial, as the quality of the input determines the effectiveness of subsequent processing techniques. Image acquisition typically involves using digital cameras, scanners, or sensors, which capture visual information and store it in a pixel-based format. Each pixel represents a small part of the image, containing data about brightness and color. A well-captured image provides a strong foundation for the processing tasks that follow.
2.2 Enhancing Image Quality with Processing Techniques
Once an image is acquired, digital image processing techniques are applied to improve its quality. Enhancements might involve adjusting brightness and contrast, reducing noise, or correcting color imbalances. These processes ensure that the final image is visually appealing and accurately represents the subject. For example, a poorly lit photo can be transformed into a vibrant, well-balanced image using brightness and contrast adjustments. Similarly, sharpening filters can enhance the edges of objects, making details more pronounced. Such improvements are essential for both artistic and technical applications.
| Algorithm Name | Purpose | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) | Feature extraction and object recognition | Face detection, object classification, and scene understanding |
| Gaussian Blur | Reducing image noise and detail | Smoothing images, preprocessing for edge detection |
| Canny Edge Detection | Identifying edges in an image | Object detection, image segmentation, and feature extraction |
| Histogram Equalization | Enhancing contrast in images | Improving visibility in low-light images and medical imaging |
| Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) | Converting spatial data to frequency domain | Image filtering, compression, and noise reduction |
| K-Means Clustering | Segmenting image regions | Image compression, object tracking, and texture analysis |
| Hough Transform | Detecting geometric shapes | Line, circle, and ellipse detection in industrial and medical imaging |
| Non-Local Means (NLM) Denoising | Reducing noise while preserving details | Enhancing image quality in photography and medical imaging |
| Bilateral Filtering | Edge-preserving smoothing | Noise reduction in images with high-texture areas |
| Principal Component Analysis (PCA) | Dimensionality reduction and feature extraction | Image compression and data visualization |
2.3 The Role of Algorithms in Transforming Visuals
At the heart of digital image processing lies the use of algorithms. These mathematical models are designed to analyze, manipulate, and enhance digital images. Algorithms play a crucial role in tasks like resizing, cropping, and applying filters. More advanced algorithms are used for specialized processes such as edge detection, object recognition, and noise reduction. For instance, an algorithm might analyze an image to detect and sharpen edges while suppressing unwanted artifacts. This level of precision allows photographers to achieve results that would be impossible with manual techniques alone.

Digital image processing relies on these foundational principles to ensure that every image reaches its full potential. By understanding and leveraging these processes, photographers and creators can elevate their work to new heights. With its ability to refine, enhance, and transform visuals, digital image processing has become an indispensable tool in the modern photographic workflow.
3. Key Techniques in Digital Image Processing
3.1 Image Filtering for Noise Reduction
One of the fundamental techniques in digital image processing is noise reduction through image filtering. Noise, often caused by low light or sensor limitations, appears as random variations in brightness or color across an image. Filtering techniques like Gaussian blur and median filtering smooth out these imperfections, improving image quality without losing essential details. Advanced noise reduction methods use algorithms to selectively target and remove noise while preserving the image’s texture and clarity, making them a vital tool for photographers and designers.
| Option/Tool Name | Purpose | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Sharpen | Applies sharpening while reducing noise and halos | Ideal for fine-tuning details in portraits, landscapes, and macro shots |
| Unsharp Mask | Enhances edges by increasing contrast between pixels | Suitable for general sharpening of moderately detailed images |
| High Pass Filter | Highlights edges and enhances detail when combined with blend modes | Best for controlled sharpening in high-contrast areas |
| Sharpen Tool | Allows localized sharpening in specific areas | Perfect for selectively enhancing fine details like eyes or jewelry |
| Shake Reduction | Reduces blur caused by camera motion and stabilizes edges | Useful for correcting slightly blurry photos due to movement |
| Edge Detection in Select and Mask | Identifies and refines edges in selections using edge-aware detection | Excellent for isolating subjects with fine details like hair or fur |
| Filter > Stylize > Find Edges | Converts edges into bold outlines by detecting abrupt pixel intensity changes | Ideal for creating artistic effects or identifying key edges |
| Filter > Other > Maximum | Expands and emphasizes bright areas, often sharpening highlights | Effective for preparing mask edges for further refinement |
| Luminosity Mask Sharpening | Sharpening based on tonal range to preserve natural contrast | Great for landscape and architectural photography with varying light levels |
| Camera Raw Filter > Details Tab | Provides controls for global sharpening and edge masking | Useful for non-destructive sharpening with real-time previews |
3.2 Color Correction and White Balance Adjustments
Color correction is another crucial aspect of digital image processing that ensures colors in an image appear natural and true to life. Poor lighting conditions or incorrect camera settings often lead to color casts, where the entire image takes on an unwanted hue. White balance adjustments correct these issues by aligning colors with the light source's temperature, such as warm indoor lighting or cool daylight. Additionally, saturation and vibrancy adjustments can be used to make colors pop, giving the image more visual appeal without looking over-edited.
3.3 Image Resizing and Resolution Management
Digital image processing enables seamless resizing of images without compromising their quality. Techniques like interpolation are used to add or remove pixels intelligently, ensuring the resized image remains sharp and clear. Resolution management is especially important for photographers and businesses that need to adapt images for various platforms, from social media to large-format printing. Proper resizing maintains image integrity and ensures it looks professional regardless of its size.
3.4 Sharpening and Edge Detection for Crisp Photos
Sharpening is a key technique used to enhance the details in an image, making it appear clearer and more defined. Digital image processing tools apply sharpening filters that increase contrast along edges, which are areas where light intensity changes abruptly. Edge detection algorithms, such as the Sobel or Canny methods, go a step further by identifying and emphasizing the boundaries of objects within the image. This is especially useful for applications like object recognition, architectural photography, and detailed close-ups.
These key techniques in digital image processing allow photographers and creators to transform raw images into polished works of art. By mastering these processes, you can ensure your photos stand out with clarity, vibrancy, and professional quality.
4. Applications of Digital Image Processing in Photography
4.1 Retouching Portraits and Correcting Flaws
One of the most popular applications of digital image processing is portrait retouching. Photographers use advanced tools to enhance facial features, remove blemishes, and even out skin tones, resulting in polished and professional-looking portraits. Techniques like frequency separation allow for detailed skin texture preservation while correcting imperfections. Additionally, digital image processing makes it easy to adjust lighting, reduce shadows, and refine details like hair or eye color. These capabilities ensure that every portrait exudes confidence and quality, making it ideal for personal, commercial, and editorial use.
4.2 HDR Imaging for High-Quality Results
High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging is another essential application of digital image processing. HDR techniques combine multiple images captured at different exposure levels into a single photo. This process ensures that both shadows and highlights retain their details, creating a balanced and dynamic image. HDR is especially useful for landscape and architectural photography, where lighting conditions can vary widely within a scene. By leveraging digital image processing tools, photographers can create stunning HDR images that showcase vibrant colors and intricate details.
4.3 Restoring and Digitizing Vintage Photos
Digital image processing also plays a critical role in preserving and restoring old or damaged photographs. Using specialized techniques, faded colors can be revived, scratches and tears can be removed, and overall image clarity can be enhanced. This process not only brings new life to precious memories but also allows them to be digitized for long-term storage and sharing. Modern software tools simplify this restoration process, enabling photographers and enthusiasts to save historical photos from deterioration and pass them on to future generations.
4.4 Creative Effects and Artistic Transformations
For photographers and artists looking to push boundaries, digital image processing offers endless creative possibilities. Filters, overlays, and artistic transformations can be applied to create surreal, abstract, or painterly effects. These techniques allow for the exploration of new artistic directions and help creators stand out in competitive fields like advertising and social media. Digital image processing ensures that creative ideas can be executed with precision, making it a powerful tool for artistic expression.
Through these diverse applications, digital image processing demonstrates its versatility and indispensability in modern photography. Whether enhancing portraits, creating HDR masterpieces, or restoring treasured memories, it continues to elevate the art and science of photography.
5. How Digital Image Processing Shapes Creative Expression
5.1 Transforming Landscapes with Advanced Editing
Digital image processing has revolutionized the way photographers approach landscape photography. By using techniques like exposure blending, color grading, and detail enhancement, photographers can transform a flat or dull scene into a vibrant masterpiece. Advanced editing tools allow for precise adjustments to shadows and highlights, ensuring that every part of the image is perfectly lit and balanced. Moreover, color grading can be used to set a mood, from warm golden hues for sunsets to cool tones for snowy landscapes. This level of control enables photographers to convey emotion and atmosphere with greater impact.

5.2 The Rise of AI-Powered Artistic Filters
Artificial intelligence has brought new dimensions to digital image processing, particularly in the realm of artistic expression. AI-powered filters and tools analyze images and apply creative effects inspired by renowned art styles or entirely new concepts. For instance, a landscape photo can be transformed into a watercolor painting, or a portrait can take on the texture of an oil canvas. These filters allow creators to experiment with different styles effortlessly, making digital image processing a playground for innovation. This capability not only expands creative horizons but also helps photographers create unique, eye-catching visuals for their audiences.
| AI-Powered Artistic Filter |
Purpose |
Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Style Transfer |
Applies artistic styles from famous artworks or patterns |
Transforming photos into painterly or abstract masterpieces |
| Colorize |
Adds or enhances color in black-and-white photos |
Reviving vintage photos or experimenting with new color palettes |
| Depth Blur |
Simulates depth of field by blurring backgrounds |
Creating professional-looking portraits or isolating subjects |
| Skin Smoothing |
Reduces blemishes and refines skin texture |
Enhancing portraits while maintaining a natural appearance |
| Makeup Transfer |
Transfers makeup styles from one photo to another |
Applying creative or realistic makeup effects for fashion or editorial shoots |
| Harmonization |
Matches color tones between different layers or compositions |
Seamlessly blending subjects into new backgrounds or composites |
| Super Zoom |
Enhances image resolution while maintaining detail |
Enlarging images for printing or cropping without losing quality |
| Landscape Mixer |
Combines elements of different landscapes into one |
Creating surreal or highly customized landscape imagery |
| Artistic Portrait |
Adds artistic effects like pencil sketch, ink, or watercolor |
Stylizing portraits for creative projects or social media content |
| Smart Portrait |
Adjusts facial expressions, lighting, and gaze direction |
Subtly or dramatically altering portrait features for creative or corrective purposes |
5.3 Experimenting with Surreal and Abstract Effects
For photographers and artists aiming to break away from realism, digital image processing provides a rich array of tools for creating surreal and abstract works. Techniques such as double exposure, glitch effects, and distortion can turn ordinary photos into imaginative compositions. These methods allow creators to play with perception, combining elements in unexpected ways or distorting reality to evoke curiosity and wonder. For instance, layering multiple exposures can create dreamlike scenes, while glitch effects add a modern, edgy aesthetic. Digital image processing makes it easy to explore these techniques, offering endless possibilities for artistic innovation.
5.4 Enhancing Storytelling Through Visual Impact
Photography has always been a medium for storytelling, and digital image processing amplifies this ability. By carefully enhancing colors, textures, and lighting, photographers can emphasize the narrative elements of an image. Whether it’s highlighting the rugged details of a weathered face or intensifying the drama of a stormy sky, digital image processing enables creators to guide viewers’ emotions and focus. This ensures that the story behind the image resonates more powerfully.
By shaping creative expression, digital image processing empowers photographers and artists to push boundaries, craft compelling visuals, and bring their unique visions to life.
6. Tools and Software for Digital Image Processing
6.1 Professional-Grade Software for Photographers
For professional photographers, advanced software tools are indispensable for achieving top-tier results. Programs like Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom are industry leaders in digital image processing, offering a comprehensive suite of features for editing and enhancing images. Photoshop provides pixel-level control for intricate adjustments, while Lightroom excels in batch processing and non-destructive editing. Other high-end tools, such as Capture One, offer superior color grading and tethered shooting capabilities, making them a favorite for studio photographers. These professional-grade programs ensure that users can manipulate every aspect of an image with precision and creativity.
6.2 Free and Accessible Tools for Beginners
Not all tools for digital image processing come with a hefty price tag. Beginners and hobbyists can access free software options that still provide powerful editing capabilities. Programs like GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program) and Darktable offer robust features for tasks like retouching, color correction, and image resizing. Additionally, Canva and Fotor provide user-friendly interfaces for quick edits, making them ideal for those new to editing or working on simpler projects. These accessible tools make it easy for anyone to start exploring the world of digital image processing without a significant financial commitment.
6.3 The Role of Mobile Apps in On-the-Go Editing
The rise of smartphones has made mobile apps a crucial component of digital image processing. Apps like Snapseed, Adobe Lightroom Mobile, and VSCO enable users to edit photos directly from their phones, offering convenience and flexibility. These apps often include features like one-touch filters, advanced color adjustments, and even AI-driven enhancements. With mobile apps, photographers can perform high-quality edits on the go, ensuring their images are ready for sharing on social media or other platforms in just minutes. This accessibility has democratized digital image processing, allowing creators at all levels to enhance their photos effortlessly.
6.4 AI-Powered Tools for Automated Enhancements
Artificial intelligence has brought significant advancements to digital image processing tools. AI-driven software like Luminar Neo and Topaz Labs simplifies complex tasks such as noise reduction, sharpening, and background removal. These tools analyze images intelligently, applying precise adjustments with minimal input from the user. For instance, AI can detect the subject of a photo and apply selective enhancements to improve focus and clarity. This automation saves time while maintaining professional results, making AI-powered tools a game-changer in the digital image processing landscape.
From professional-grade software to mobile apps and AI-driven tools, digital image processing offers a range of solutions to suit every need. By choosing the right tools, creators can elevate their work and bring their vision to life.
7. Benefits and Challenges of Digital Image Processing
7.1 Advantages in Speed, Precision, and Flexibility
One of the greatest benefits of digital image processing is the speed at which edits can be made. Compared to traditional darkroom techniques, digital tools allow photographers to apply complex adjustments in minutes. Whether it’s correcting exposure, sharpening details, or removing blemishes, digital processing is both faster and more precise. Flexibility is another significant advantage; edits can be made non-destructively, meaning changes can be reversed or adjusted without damaging the original file. This combination of speed, precision, and flexibility makes digital image processing an indispensable tool for both professional and amateur photographers.
7.2 Pushing Creative Boundaries
Digital image processing opens up endless creative possibilities. It allows photographers to experiment with different effects, such as HDR imaging, surreal compositions, and artistic filters. These tools encourage creativity, enabling photographers to push boundaries and explore new artistic directions. For instance, double exposure techniques or glitch effects can transform ordinary photos into unique works of art. By using digital tools to enhance creativity, photographers can create compelling visuals that stand out in a competitive market.
7.3 Ethical Considerations in Photo Manipulation
While digital image processing offers incredible creative power, it also raises ethical questions about photo manipulation. Over-editing or altering the essence of an image can mislead viewers, particularly in contexts like journalism or documentary photography. For example, excessive use of retouching tools in portrait photography can create unrealistic beauty standards. Photographers must strike a balance between enhancing an image and maintaining its authenticity. Transparency about edits is often essential, particularly in professional or journalistic settings.
7.4 Overcoming Technical Challenges
Digital image processing comes with its own set of challenges. High-quality processing often requires powerful hardware and specialized software, which can be expensive. Additionally, the learning curve for advanced tools like Photoshop or Capture One can be steep for beginners. File management is another common issue, as high-resolution files can consume significant storage space. However, with practice and the right resources, these challenges can be mitigated. Online tutorials, user communities, and cloud storage solutions can help photographers overcome these hurdles.
Digital image processing offers unparalleled benefits in terms of efficiency, creativity, and flexibility, but it also requires ethical mindfulness and technical proficiency. By understanding and addressing these challenges, photographers can fully harness the potential of this transformative technology.
8. The Future of Digital Image Processing in Photography
8.1 AI and Machine Learning Enhancements
The future of digital image processing is closely tied to the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies are already revolutionizing the way images are edited and enhanced, and their potential is only growing. AI-driven tools can identify subjects, analyze compositions, and apply precise adjustments with minimal user input. For example, facial recognition can isolate and retouch facial features in portraits, while object detection can identify and enhance specific elements in a scene. Machine learning models continue to improve, making digital image processing faster, smarter, and more accessible to users of all skill levels.
8.2 Trends in Real-Time Image Processing
Real-time digital image processing is an emerging trend that is transforming photography workflows. With advancements in camera technology and processing power, photographers can now apply edits as they capture images. Features like live filters, real-time noise reduction, and in-camera HDR enable creators to visualize their final output instantly. These tools not only save time but also enhance creativity by allowing photographers to experiment with effects and settings on the spot. As hardware and software continue to evolve, real-time processing is expected to become a standard feature in both professional and consumer-grade cameras.
8.3 The Ongoing Integration of AR and VR Technologies
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are reshaping the possibilities of digital image processing. These technologies combine the real world with digital enhancements, creating immersive visual experiences. For example, AR-powered apps can overlay creative effects or edits onto live camera feeds, allowing users to see processed images before capturing them. In the realm of VR, digital image processing plays a crucial role in creating high-quality 360-degree visuals for virtual environments. This integration is particularly exciting for industries like advertising, gaming, and event photography, where immersive visuals are in high demand.
8.4 Sustainability and the Future of Storage
As photography generates ever-larger image files, digital image processing must adapt to meet sustainability challenges. The development of more efficient compression algorithms and cloud-based storage solutions is essential to manage the growing volume of high-resolution content. Future advancements may focus on reducing the environmental impact of digital workflows while maintaining quality and accessibility for creators worldwide.
The future of digital image processing is poised to deliver unparalleled efficiency, creativity, and innovation. With the integration of AI, real-time processing, and immersive technologies, photographers will have tools that continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in visual storytelling.
9. Tips for Getting Started with Digital Image Processing
9.1 Essential Skills Every Photographer Should Learn
For anyone new to digital image processing, mastering a few key skills is essential. Begin with basic techniques like cropping, adjusting brightness and contrast, and correcting color imbalances. Learning how to use layers and masks in software like Photoshop can significantly expand your editing capabilities, allowing you to make precise, localized adjustments. Familiarize yourself with sharpening tools and noise reduction, as these are vital for improving image clarity. By building a strong foundation in these core skills, you’ll be well-prepared to explore more advanced techniques in the future.
9.2 Choosing the Right Tools for Beginners
Selecting the right tools is crucial for starting your journey in digital image processing. Beginner-friendly software such as Adobe Lightroom, Canva, or Snapseed offers intuitive interfaces with powerful features. These tools make it easy to apply adjustments and explore creative effects without being overwhelmed by complex options. For those on a budget, free programs like GIMP or Darktable provide robust functionality at no cost. As you gain confidence and experience, you can transition to more advanced tools like Photoshop or Capture One for greater control over your edits.
9.3 Building a Workflow for Efficient Processing
Efficiency is key in digital image processing, especially when working with large batches of images. Start by organizing your files with a consistent naming system and folder structure. Use batch processing tools to apply basic edits like resizing or exposure adjustments across multiple images at once. Develop a step-by-step workflow—such as starting with global adjustments, followed by localized corrections, and finishing with sharpening and exporting—to ensure a streamlined process. Saving presets for frequently used settings can also save time while maintaining consistency across your work.
9.4 Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When starting with digital image processing, it’s easy to over-edit or make errors that detract from your images. One common mistake is pushing saturation or contrast too far, resulting in unnatural-looking photos. Another is failing to save a copy of the original file, making it impossible to revert changes if needed. Always work on duplicates and use non-destructive editing techniques to preserve your files. Additionally, take breaks during the editing process to ensure your adjustments remain objective and balanced.
By developing essential skills, choosing the right tools, and establishing an efficient workflow, you can confidently embark on your journey into digital image processing. Avoiding common pitfalls and practicing regularly will help you create polished, professional-quality images.
10. Conclusion
10.1 The Enduring Impact of Digital Image Processing
Digital image processing has transformed the world of photography, offering unparalleled tools and techniques for enhancing, correcting, and creatively transforming images. From beginners experimenting with basic edits to professionals pushing the boundaries of artistic expression, this technology has become an essential part of modern visual storytelling. By harnessing its capabilities, photographers can achieve results that were once impossible, ensuring their work stands out in a competitive and ever-evolving field.
10.2 Embracing Technology to Elevate Your Photography
As digital image processing continues to evolve, embracing its tools and techniques is crucial for photographers seeking to grow their skills and expand their creative horizons. Whether you're using AI-driven tools for quick enhancements or exploring advanced editing techniques, the possibilities are endless. By investing time in learning and experimenting, you can unlock the full potential of your images and refine your artistic vision.
Digital image processing isn’t just about making photos look better—it’s about telling stories, evoking emotions, and bringing creative ideas to life. With its limitless potential, this powerful technology will remain at the heart of modern photography for years to come.
Thank you for visiting our site and being part of this journey with us! We rely on the generous support of visitors like you to continue providing high-quality. Your donation, no matter the size, helps us maintain the website and create more valuable resources for everyone.